Data Access and Analysis Tools¶
The Rubin Science Platform (RSP) is the set of integrated web-based applications, services, and tools to query, visualize, subset, and analyze LSST data.
Throughout DP0 the RSP will be in active development by Rubin Observatory staff, with access provided to delegates on a shared-risk basis.
See Rubin Science Platform Documentation page for additional information.
RSP usage: risks and responsibilities¶
All RSP users are responsible for being aware of the risks inherent in using software in active development, and must familiarize themselves with these risks.
Rubin Science Platform (RSP)¶
The Rubin Science Platform (RSP) provides access to Rubin Observatory data products. The Notebook Aspect enables programmatic interaction with, and analysis of, data products in a python environment. The Portal Aspect provides interactive query, data discovery, and visualization tools.
During DP0, the RSP has limited functionality (see RSP usage: risks and responsibilities) compared to the Operations-era (see the RSP Vision Document, LSE-319). During Rubin Observatory Operations, the RSP will feature additional tools in the Application Programming Interface (API) aspect and more options for using the Portal and Notebook aspects in tandem.
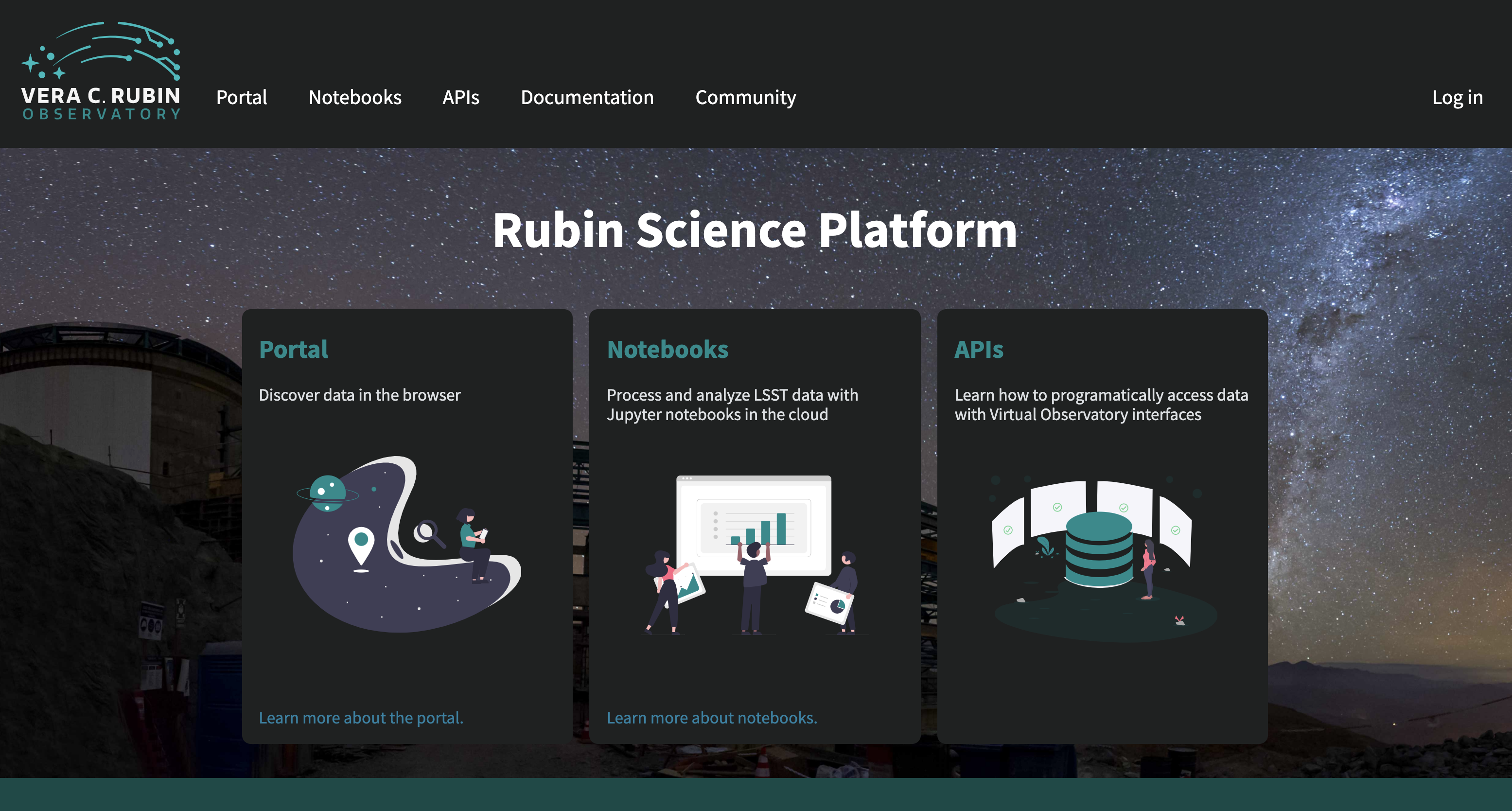
Screenshot of the data.lsst.cloud dashboard. Enter an aspect using the top menu bar or by clicking on the icon.¶
Portal Aspect¶
The Portal Aspect of the RSP provides an environment for data discovery, query, filtering, and visualization. Note that the Portal Aspect is expected to evolve significantly before the first LSST data release.
Notebook Aspect¶
The Notebook Aspect of the RSP provides Python-based access to DP0.2 data products via a custom implementation of web-based JupyterLab Notebooks (JupyterLab documentation), as well as a command-line interface.
Within the RSP Notebook Aspect users can query and retrieve data sets, manipulate and display images, calculate derived properties, plot results, reprocess data with the LSST Science Pipelines, and most other analyses you can imagine performing with Python on astronomical images and catalogs.
A stable software environment is provided and maintained for users, which includes many commonly-used packages and the LSST Science Pipelines.
For DP0, this environment will only support Python 3.
To view a list of packages available to you in the Notebook Aspect of the RSP, type pip list in a terminal.
API Aspect¶
The API (Application Programming Interface) Aspect of the RSP enables programmatic access to the Rubin data products via Virtual Observatory (VO) interfaces. Users will be able to remotely access the LSST data and DAC services using tools they’re already familiar with, e.g. TOPCAT or libraries such as Astropy. The Portal and Notebook Aspects of the RSP make use of the same APIs to internally access the LSST datasets.
The API Aspect of the RSP is very powerful and will eventually allow for federation with other astronomical archives, bringing added value to the LSST dataset.
Data processing tools¶
Documentation for the LSST Science Pipelines, a software package which is available to all RSP users via the Notebook Aspect, can be found at pipelines.lsst.io.
A brief summary of how the LSST Science Pipelines were used to create the DP0.2 data products can be found in this Data Processing Overview.